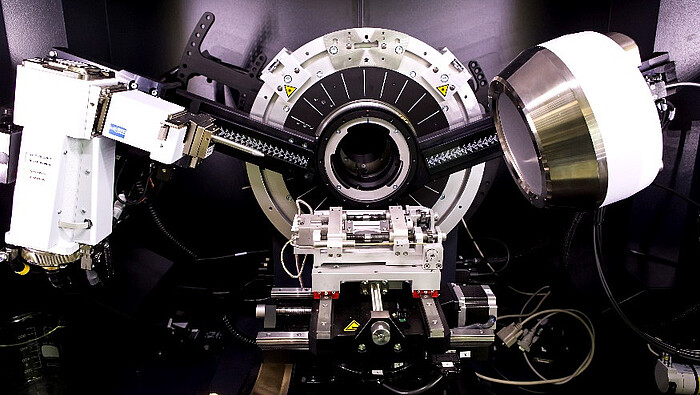
X-ray diffractometer (XRD) Bruker Discover D8
The characteristic crystal structure of materials can be made visible and analyzed by the diffraction of X-rays. Preferential orientations and residual stresses introduced by manufacturing processes can also be determined. The Institute of Materials Science has a modern X-ray diffractometer with which both minimal quantities of powder and real components can be examined.
The characteristic crystal structure of materials can be made visible and analyzed by the diffraction of X-rays. Preferential orientations and residual stresses introduced by manufacturing processes can also be determined. The Institute of Materials Science has a modern X-ray diffractometer with which both minimal quantities of powder and real components can be examined.
Technical equipment
- Parallel radiation with Cu, Co or Cr X-ray source
- Exit apertures: 2 mm, 1 mm, 0.5 mm, 0.3 mm
- xyz sample stage with chi-tilt and phi-rotation
- Camera-supported double laser unit for sample alignment
- 2D surface detector
- Max. Sample weight 5 kg
- Compatible with µ-train pressure module
Measurement methods:
- Phase analysis
- Texture analysis
- Determination of residual stress

30823 Garbsen