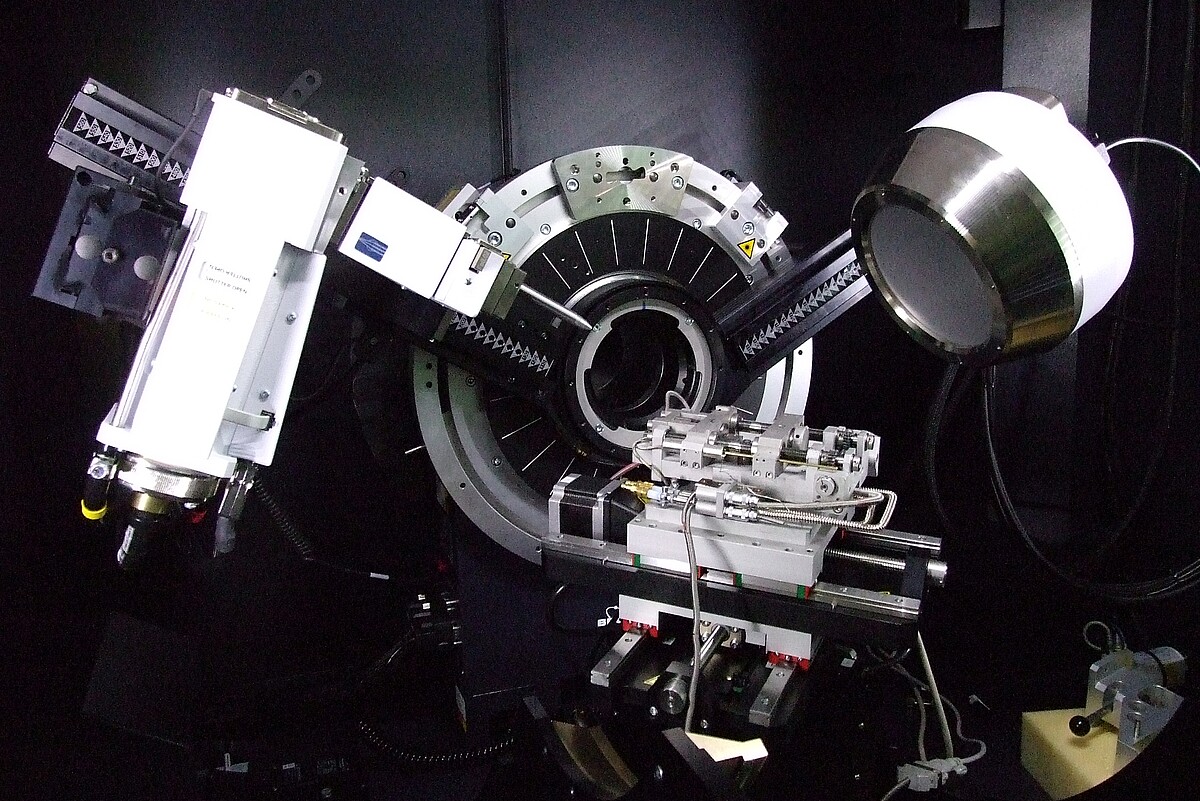
Through in-situ experiments, one aims to gain insight into the microstructural processes within the material, for example, during deformation or significant temperature changes – and all this while it is happening! Using a miniature tensile-compression module, samples can be subjected to mechanical loading and heating, for instance, under the scanning electron microscope or the X-ray diffractometer. This allows the observation and quantification of phase transformations, or the identification of strain locations through digital image correlation (DIC) from the resulting images.
Through in-situ experiments, one aims to gain insight into the microstructural processes within the material, for example, during deformation or significant temperature changes – and all this while it is happening! Using a miniature tensile-compression module, samples can be subjected to mechanical loading and heating, for instance, under the scanning electron microscope or the X-ray diffractometer. This allows the observation and quantification of phase transformations, or the identification of strain locations through digital image correlation (DIC) from the resulting images.
CONTACT TO THE MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY DIVISION


30823 Garbsen